Setting up an AWS account and IAM permissions
Best practice, avoid using Root User. Instead, create an IAM Role with minimal permissions for Lambda to access DynamoDB, ensuring security and ease of management.
In this section, we will create an IAM Role and Policy to allow Lambda functions (getPosts and createPost) to interact with the BlogPosts table in DynamoDB, limited to the us-east-1 region (or your chosen region).
1. Access the AWS IAM Management Console
- Log in to the AWS Management Console.
- Access IAM Console
2. Create Custom Policy
2.1. In the left navigation bar, select Policies
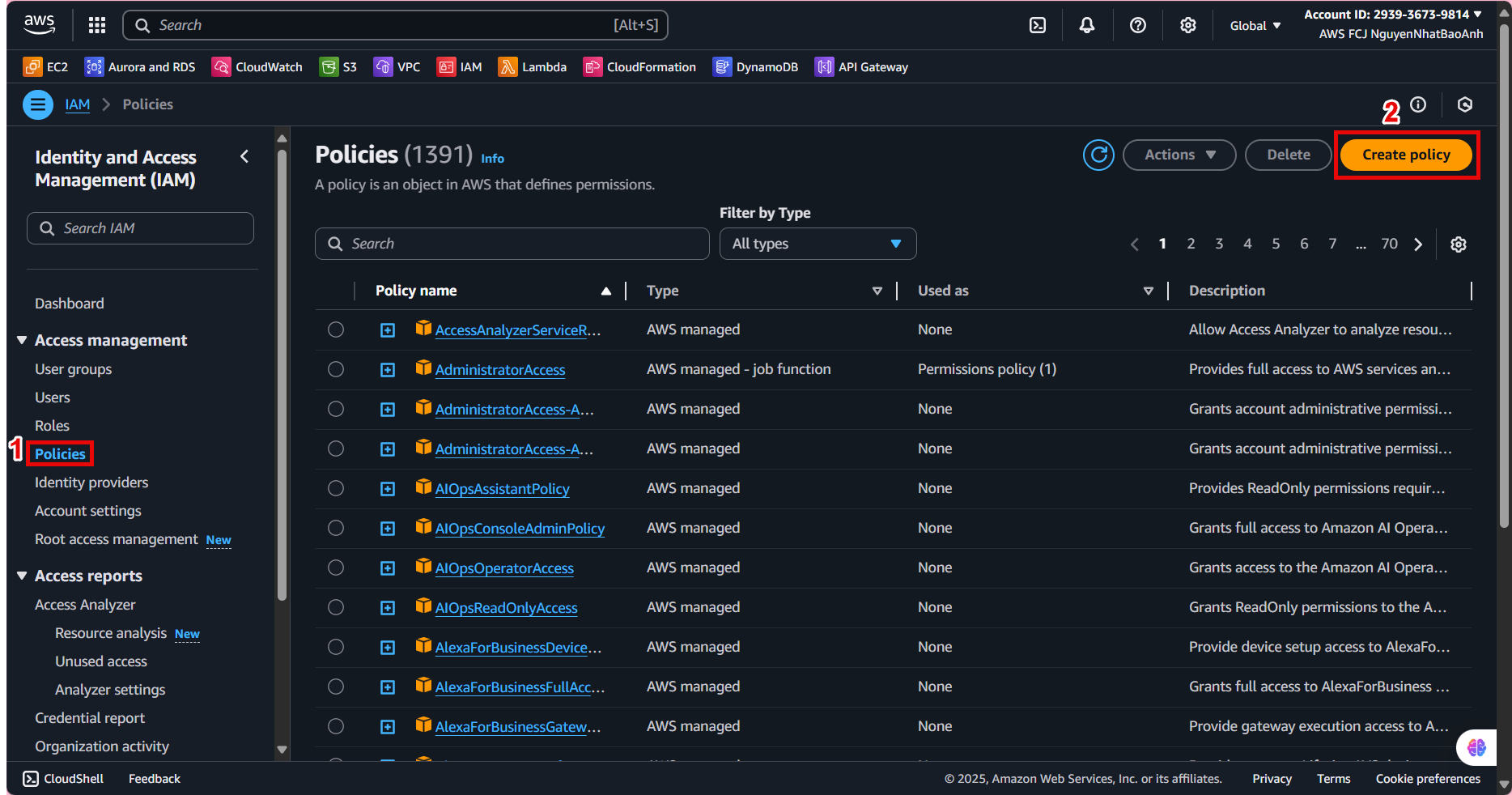
2.2. At the Policies interface, select Create policy.
2.3. Step 1 - Specify permissions
Select JSON tab and paste the JSON below into Policy Editor, then select Next:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:Scan",
"dynamodb:PutItem"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb:us-east-1:*:table/BlogPosts",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:RequestedRegion": "us-east-1"
}
}
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
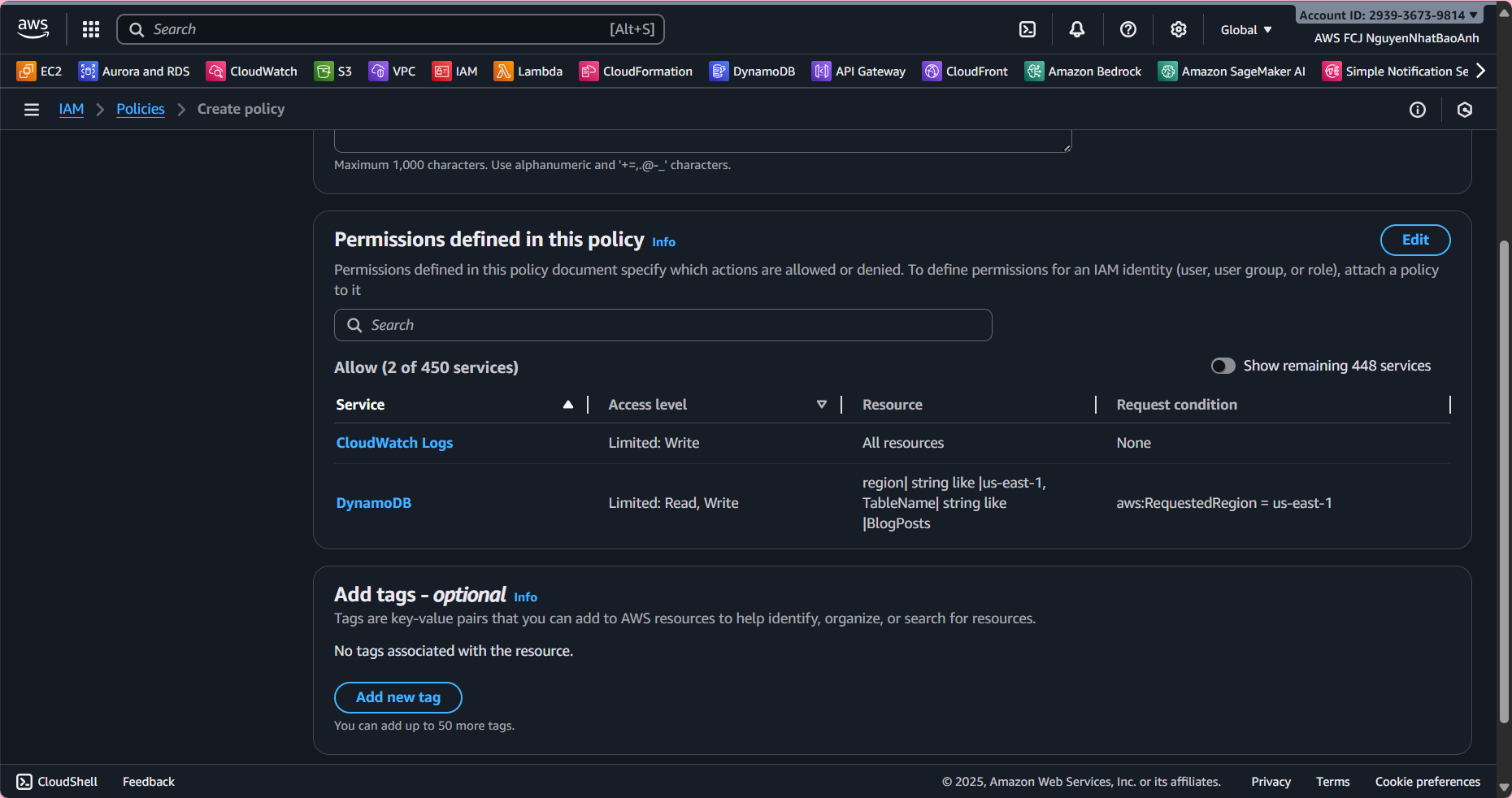
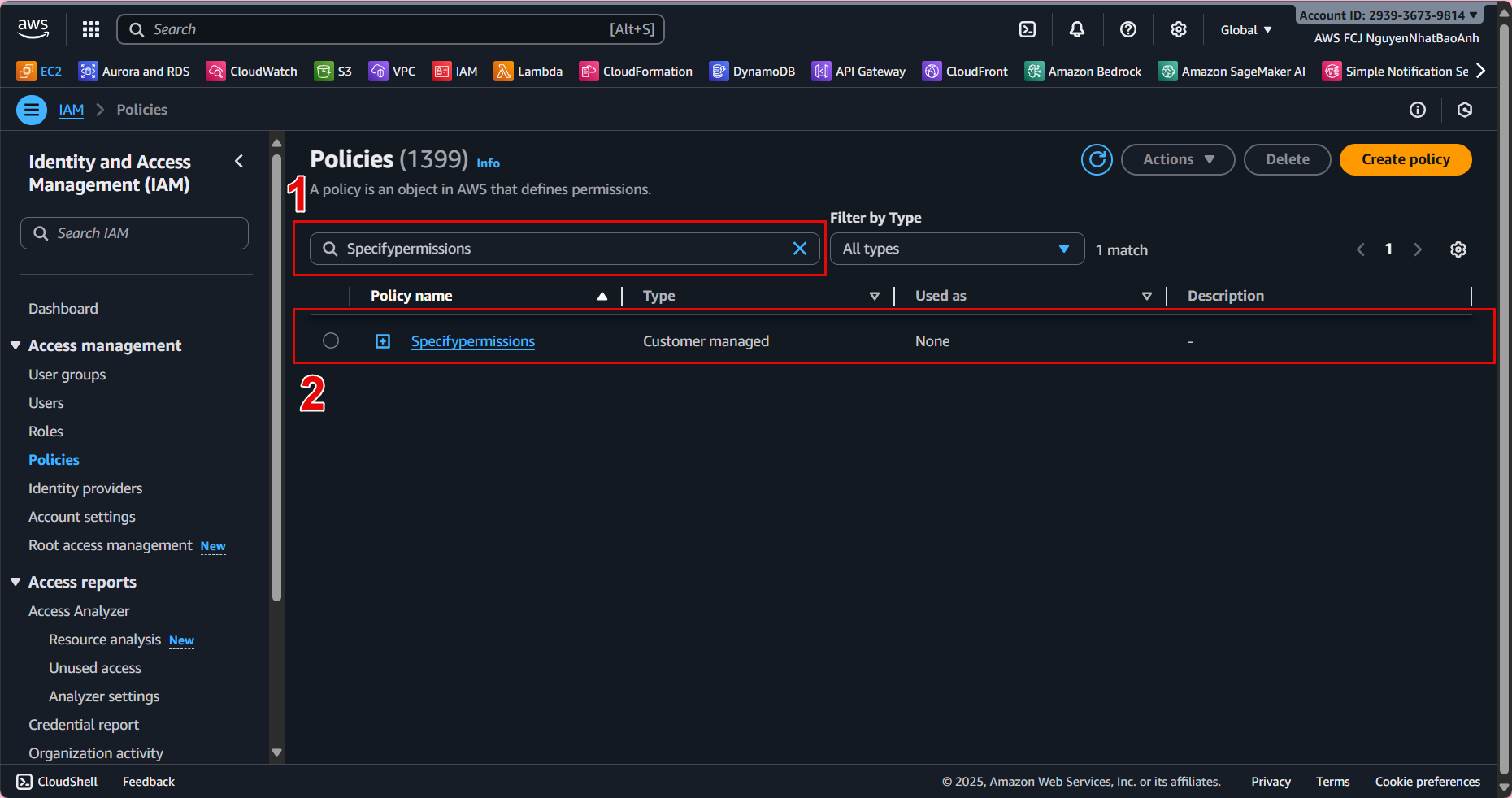
This policy allows Lambda to perform dynamodb:Scan (get posts) and dynamodb:PutItem (create posts) on the BlogPosts table in the us-east-1 region. CloudWatch Logs permissions allow Lambda to write logs.
3. Create IAM Role for Lambda
IAM Role is assigned to Lambda functions to grant access. The lambda-dynamodb-access policy will be attached to this role.
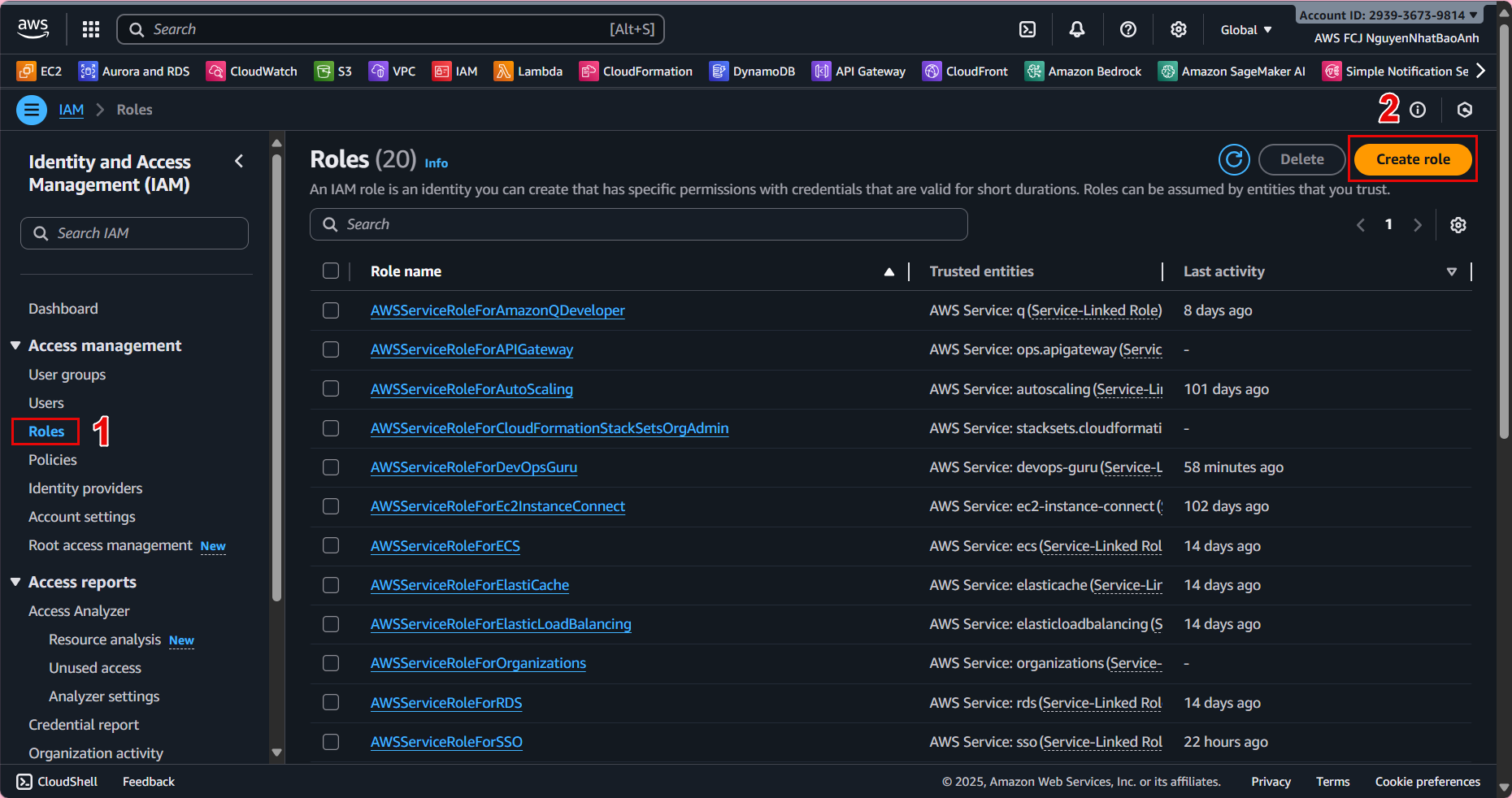
- 3.1. Go to Roles in the IAM Console.
- 3.2. Select Create role.
- 3.3. In the Create role interface:
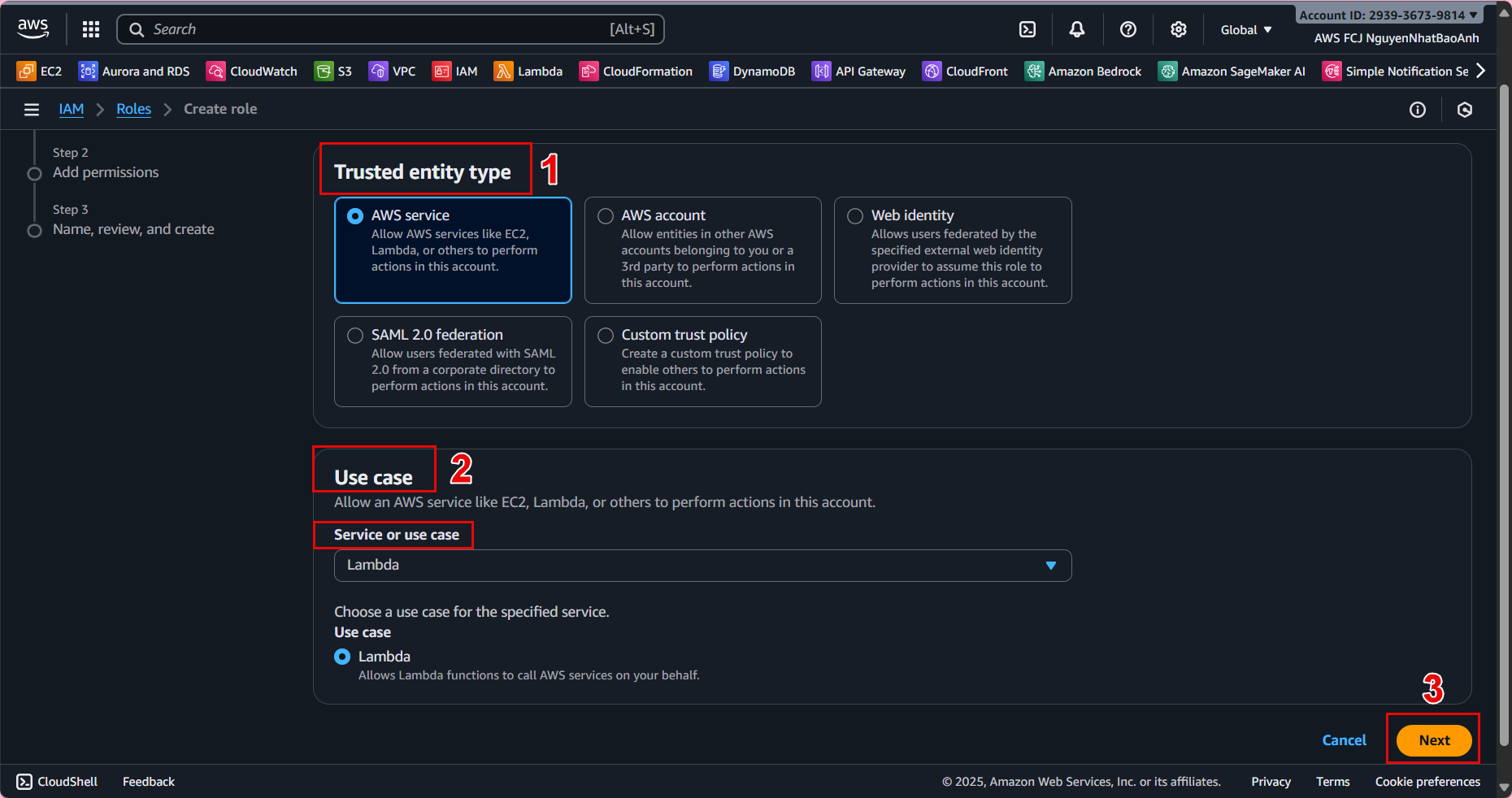
Select AWS service as the trusted entity type. Select Lambda in the use case. Click Next.
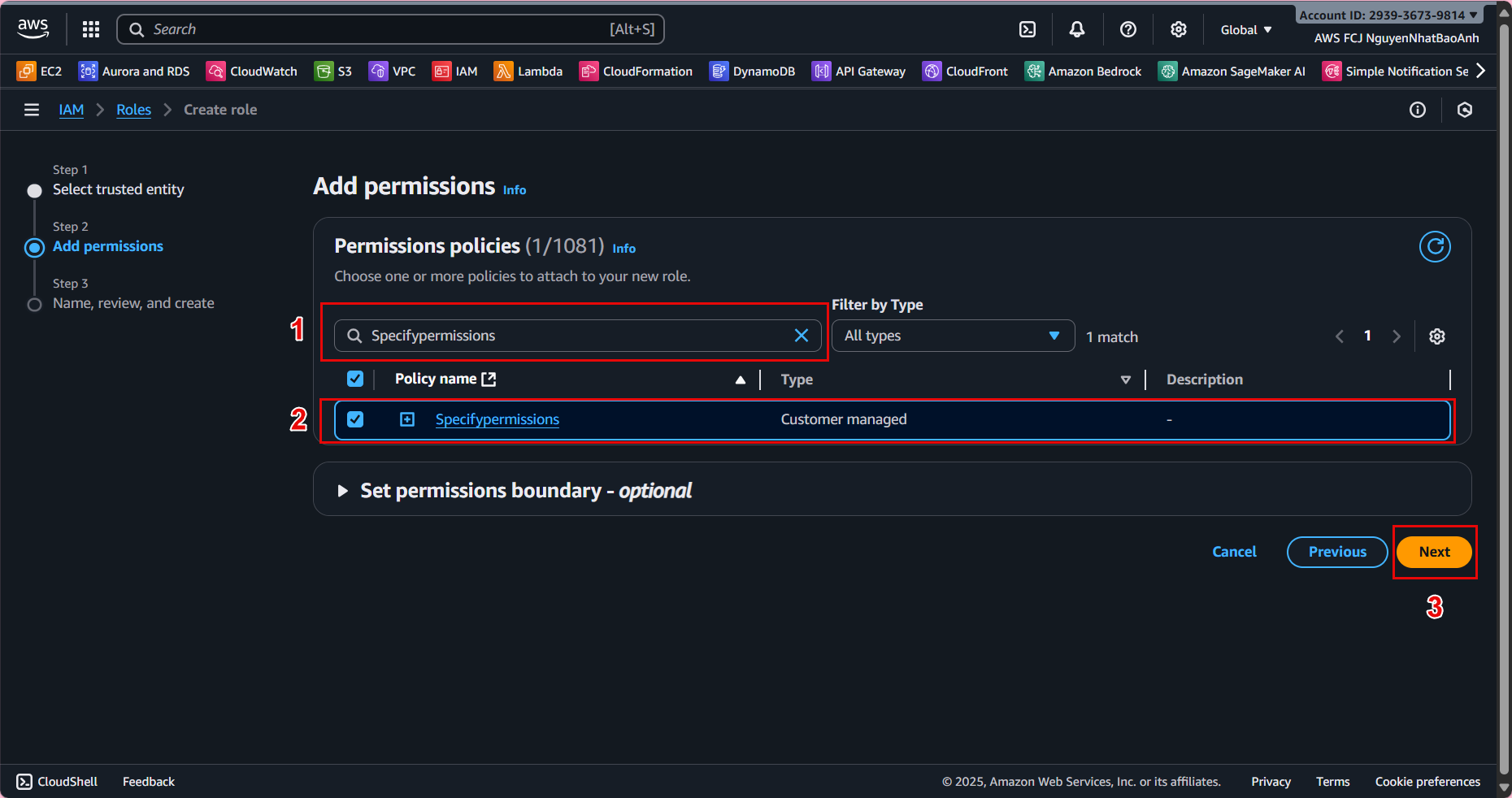
- 3.4. In Add permissions:
Find and select the lambda-dynamodb-access policy. (Optional) Add AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole for basic CloudWatch Logs permissions. Click Next.
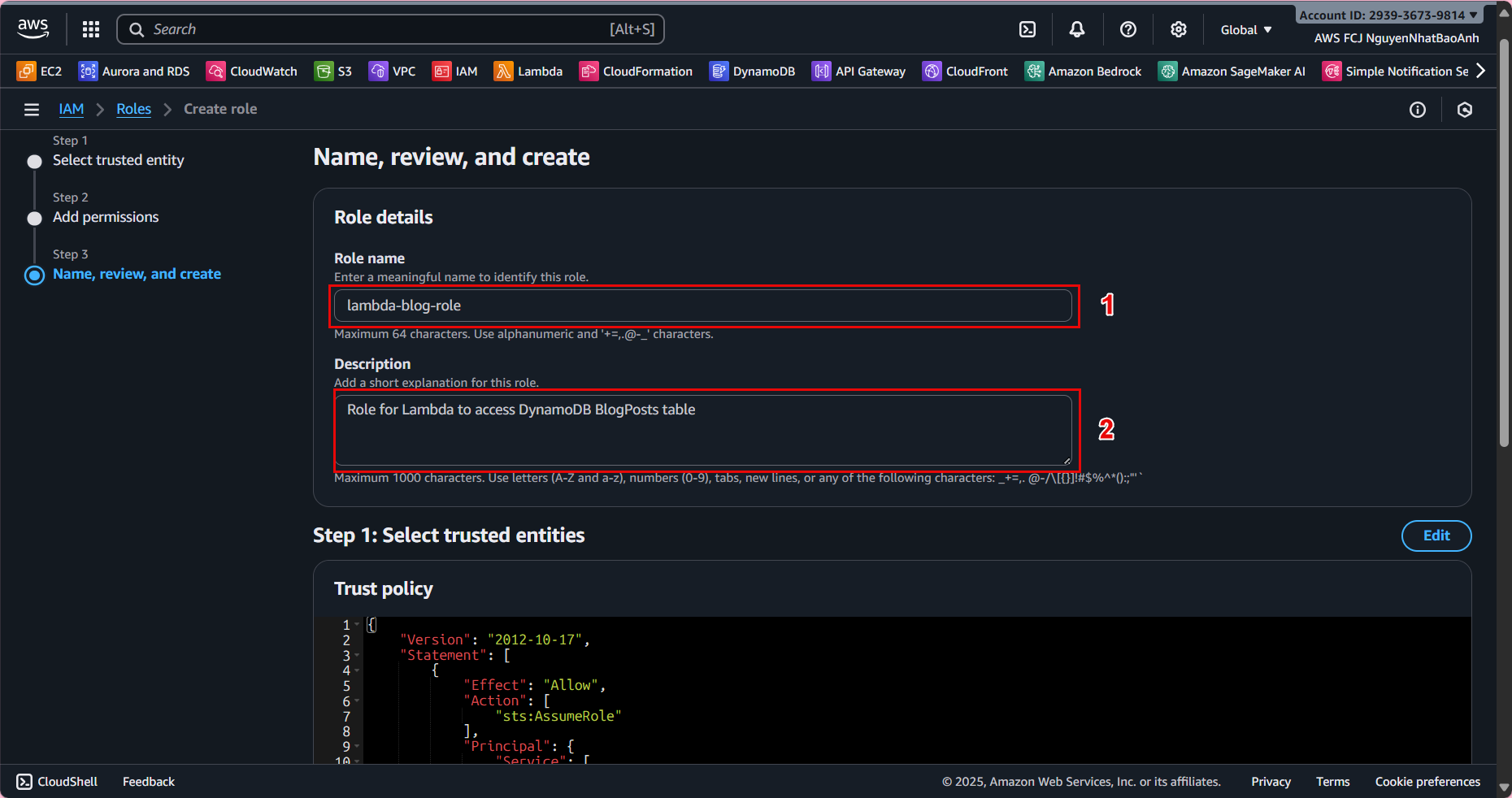
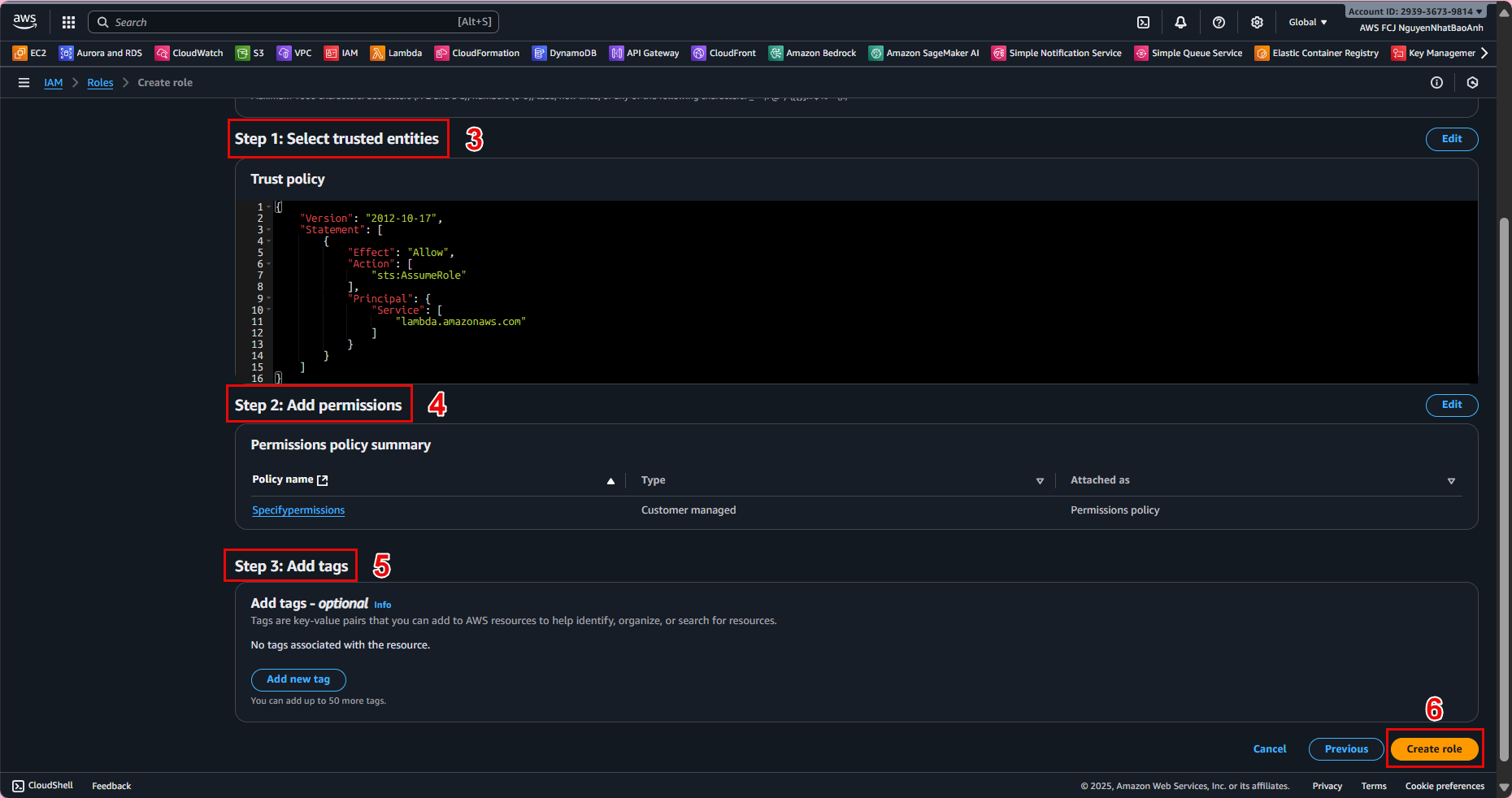
- 3.5. In Name, review, and create:
Role name: lambda-blog-role. Description: Role for Lambda to access DynamoDB BlogPosts table. Click Create role.
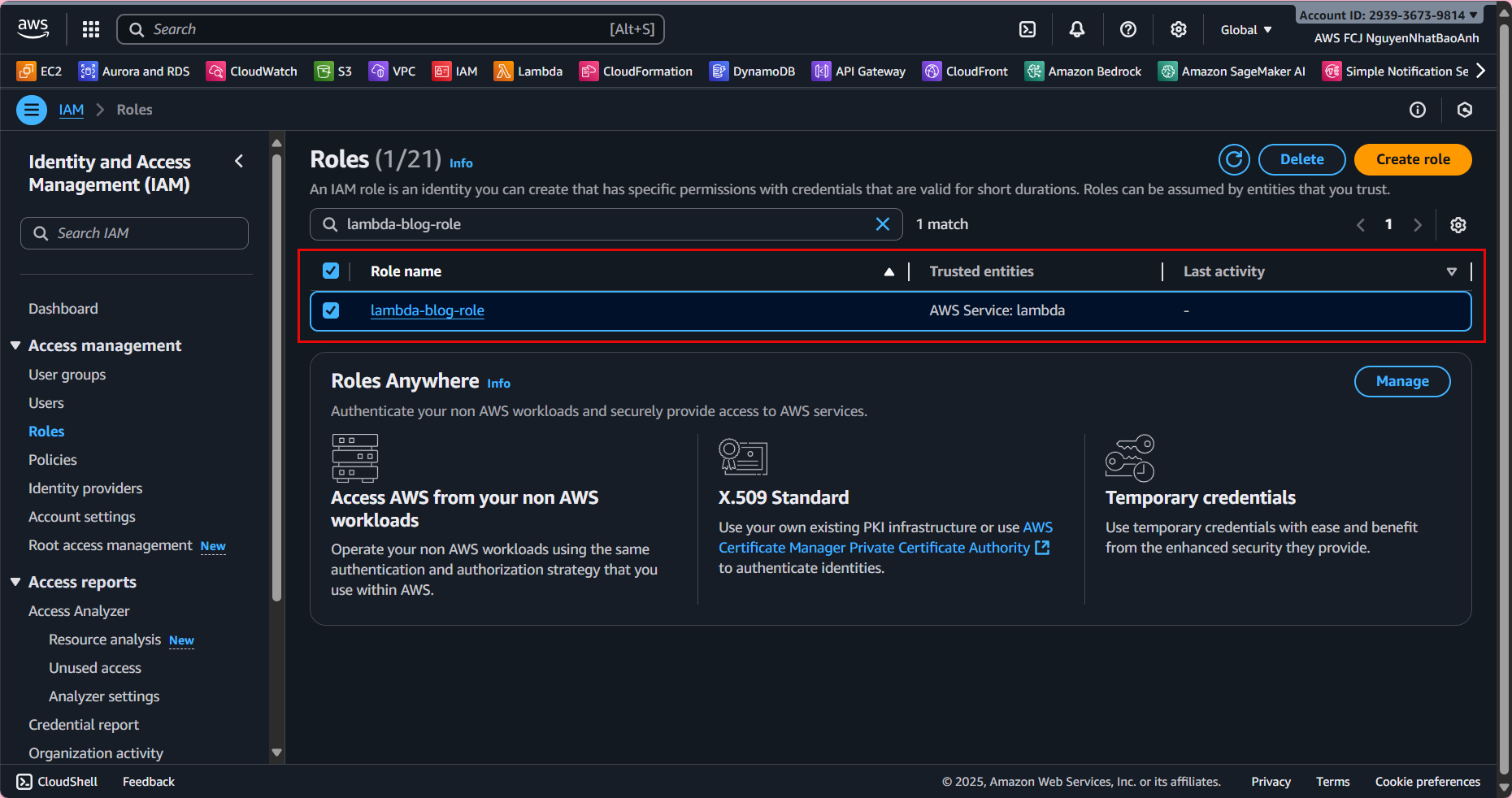
4. Assign IAM Role to Lambda Functions
- 4.1. Go to the Lambda Console.
- 4.2. Open the getPosts function:
Go to Configuration → Permissions. Click Edit on the execution role. Choose Existing role → lambda-blog-role. Save.
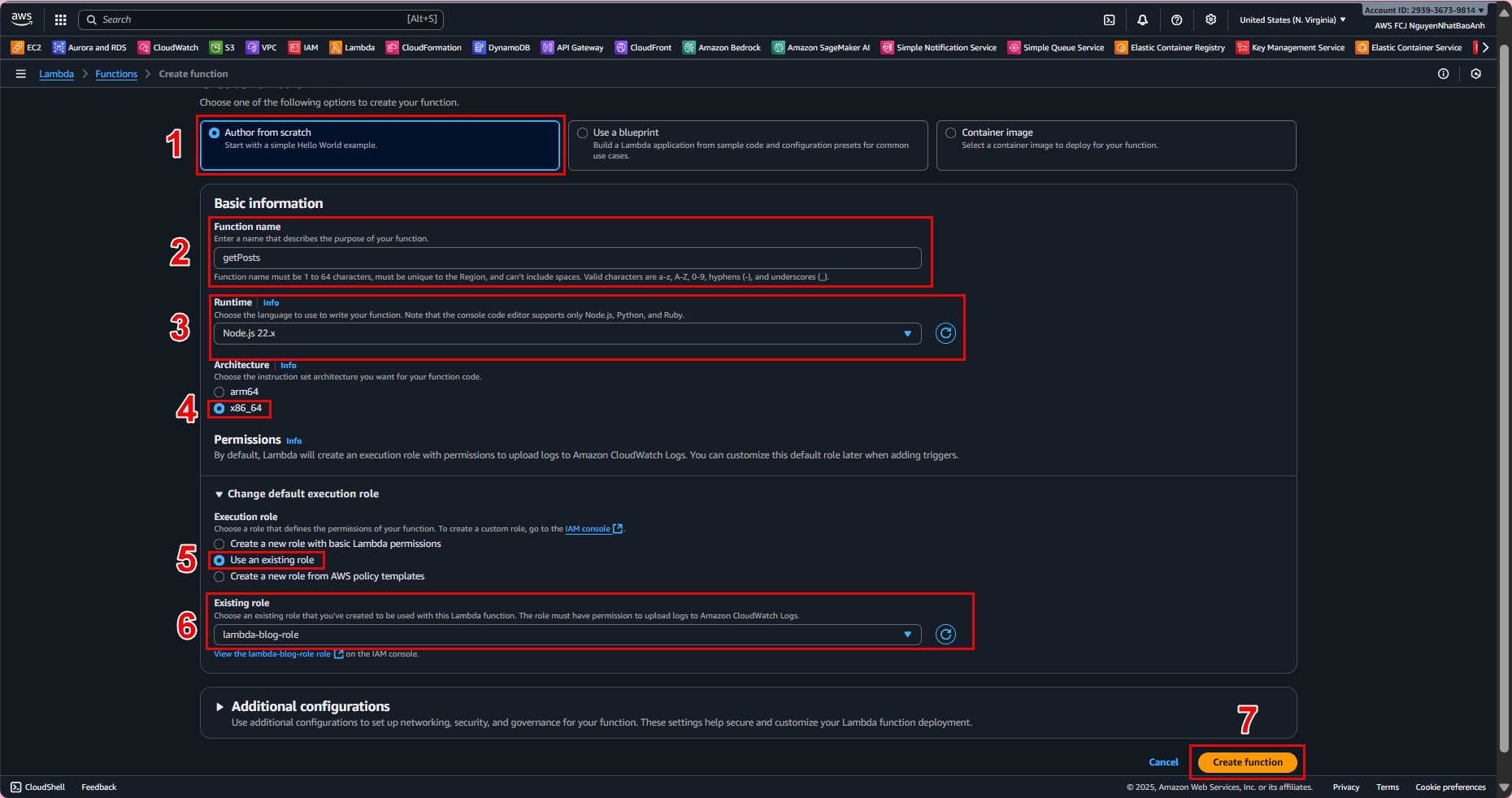
- 4.3. Repeat for the createPost function.
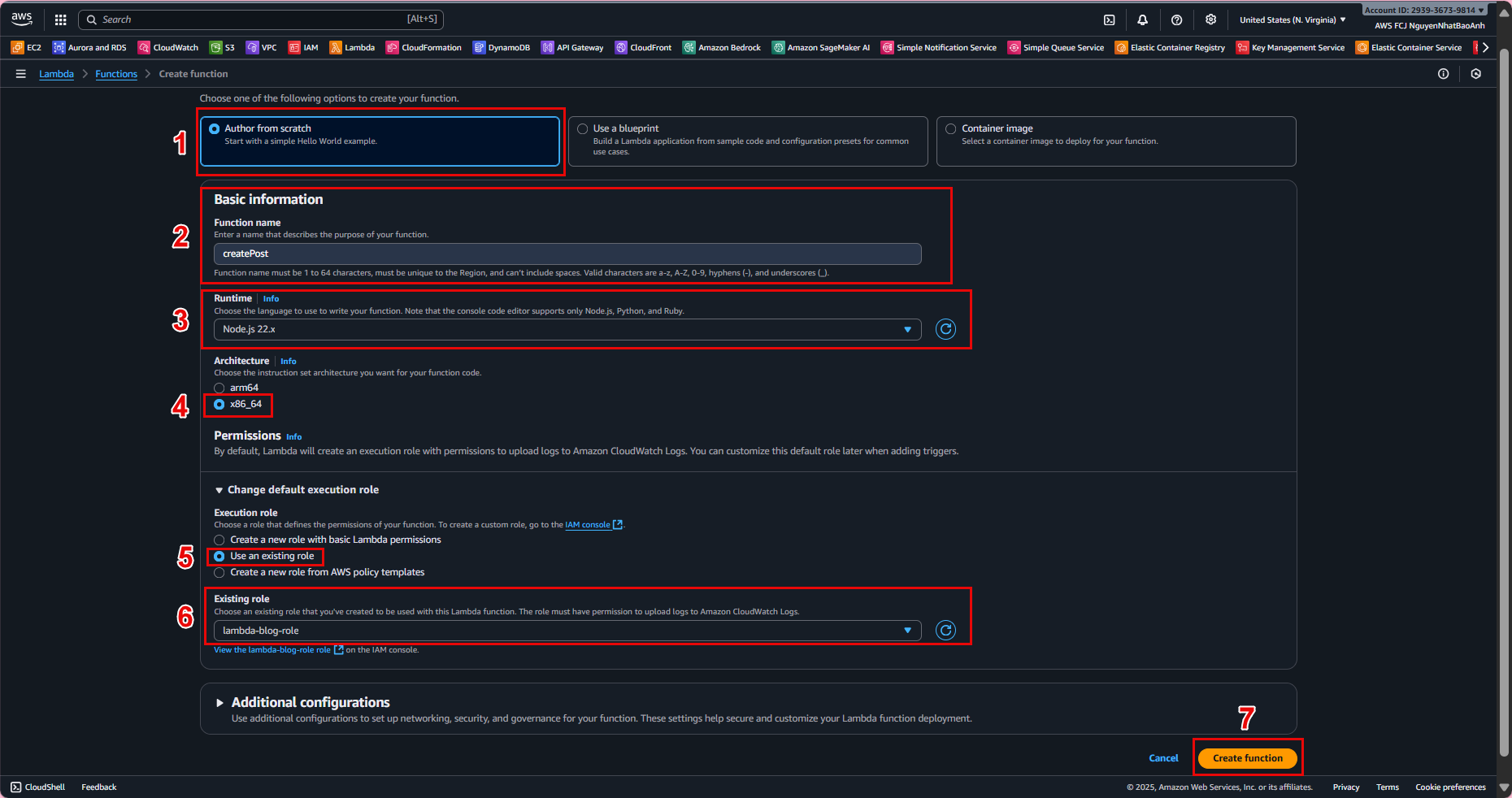
- 4.4. Verify in the IAM Console:
Open the lambda-blog-role. Ensure the lambda-dynamodb-access policy is attached. Confirm the DynamoDB ARN matches your table.
5. Test the IAM Role with Lambda
- 5.1. Log in with an IAM User (not Root).
- 5.2. Test getPosts function in Lambda:
Go to the Test tab, create an event with {}. Click Test. Expected result:
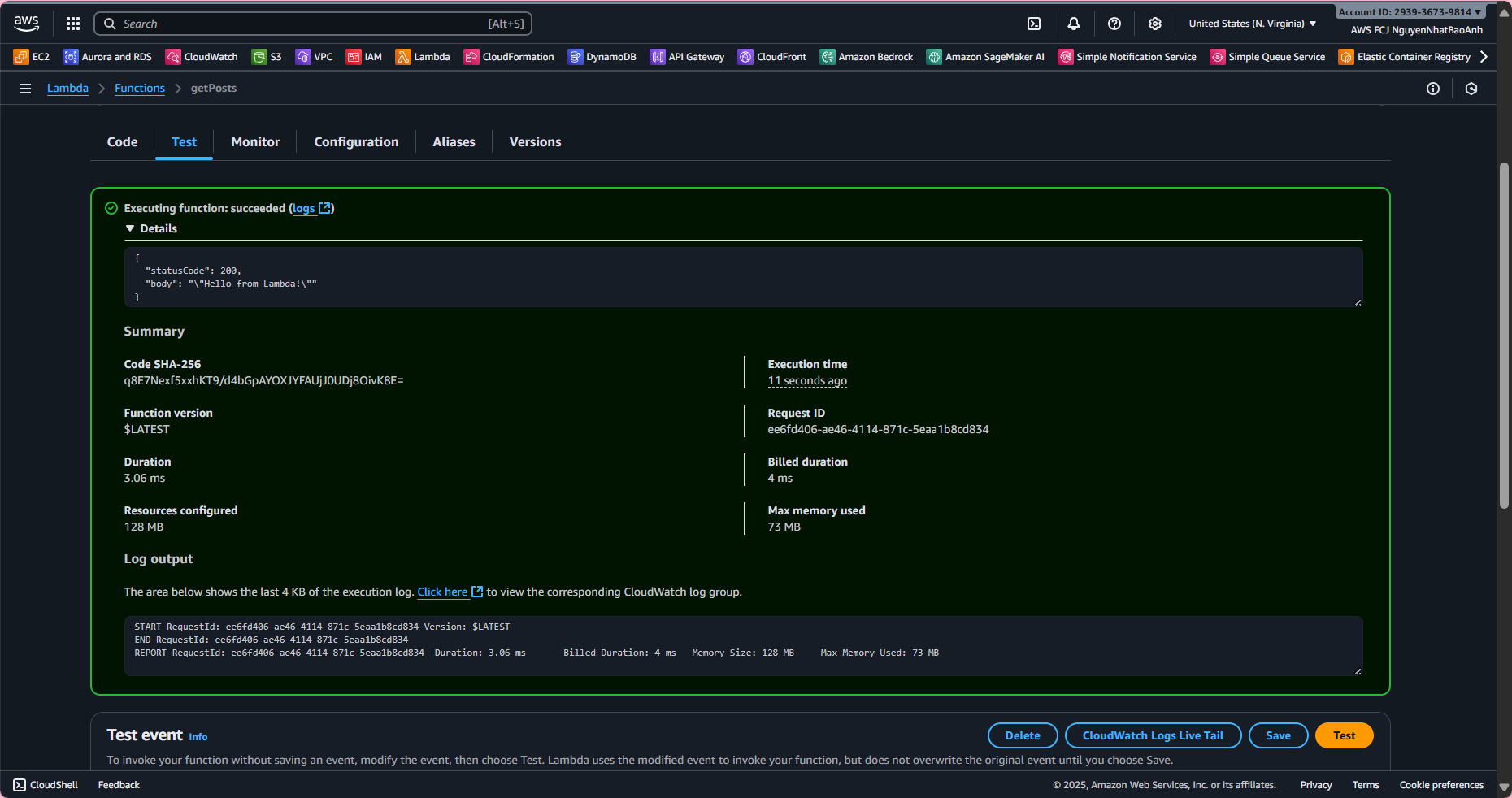
{
"statusCode": 200,
"body": "[]",
"headers": { "Content-Type": "application/json" }
}
(or existing posts if the table has data).
- 5.3. If AccessDenied errors appear:
Check CloudWatch Logs. Verify ARN matches your table. Confirm region = us-east-1. Ensure environment variable TABLE_NAME=BlogPosts.
Done! You have created an IAM Role and Policy for Lambda to access DynamoDB.